Azure multi subscriptions
The Azure multi-subscription sync solution provides a way to periodically sync resources from multiple Azure subscriptions into Port with these key advantages:
- No infrastructure required - runs directly via GitHub Actions or locally
- Multi-subscription support - sync resources across all your Azure subscriptions from a single deployment
- Near real-time updates - incremental syncs every 15 minutes by default
- Full control - customize which resource types to include and how they're mapped
- Zero setup complexity - ideal for large organizations wanting near real-time data without complex infrastructure
Overview
This solution:
- Is written in Python using the Azure SDK for Python.
- Runs as a GitHub workflow at configurable periodic intervals.
- Provides two sync modes:
- Incremental: Syncs recent changes (default: every 15 minutes).
- Full: Complete sync of all resources (recommended for initial setup).
- Prioritizes Azure resources with detailed tracking.
- Supports flexible data mapping through Port webhooks.
- Can be deployed via:
- GitHub Actions for automated periodic sync.
- Local installation for development and testing.
The source code is available in the port-labs/incremental-sync repository.
Azure setup
This integration requires the standard Azure app registration setup.
Keep the following credentials handy after setup:
AZURE_CLIENT_ID: The client ID of the Azure service principalAZURE_CLIENT_SECRET: The client secret of the Azure service principalAZURE_TENANT_ID: The tenant ID of the Azure service principal
Azure App Registration Setup
To ingest resources from Azure, you will need to create an Azure App Registration and assign it read permissions to the resources you want to ingest.
- Create an Azure App Registration in the Azure portal.
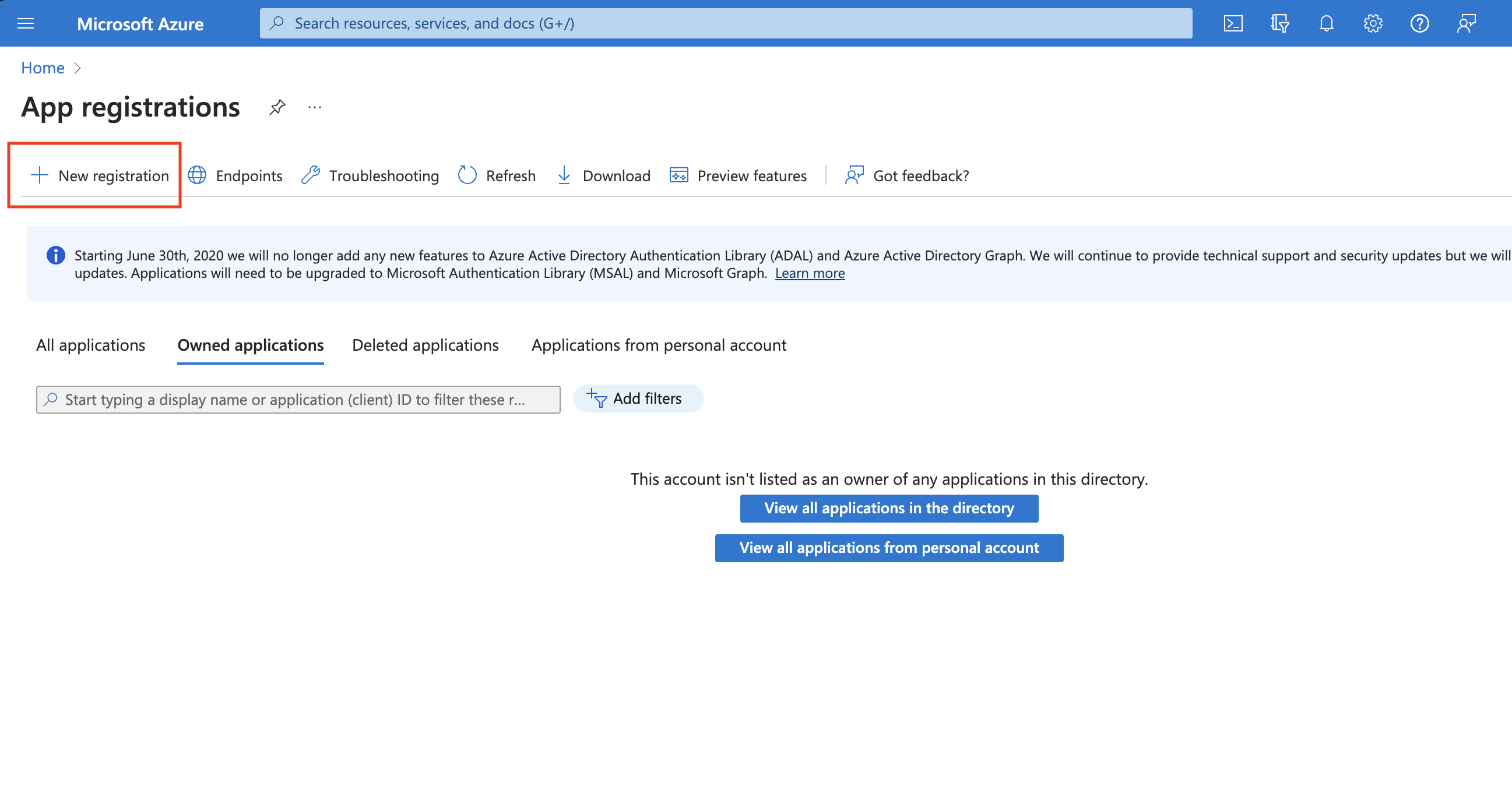
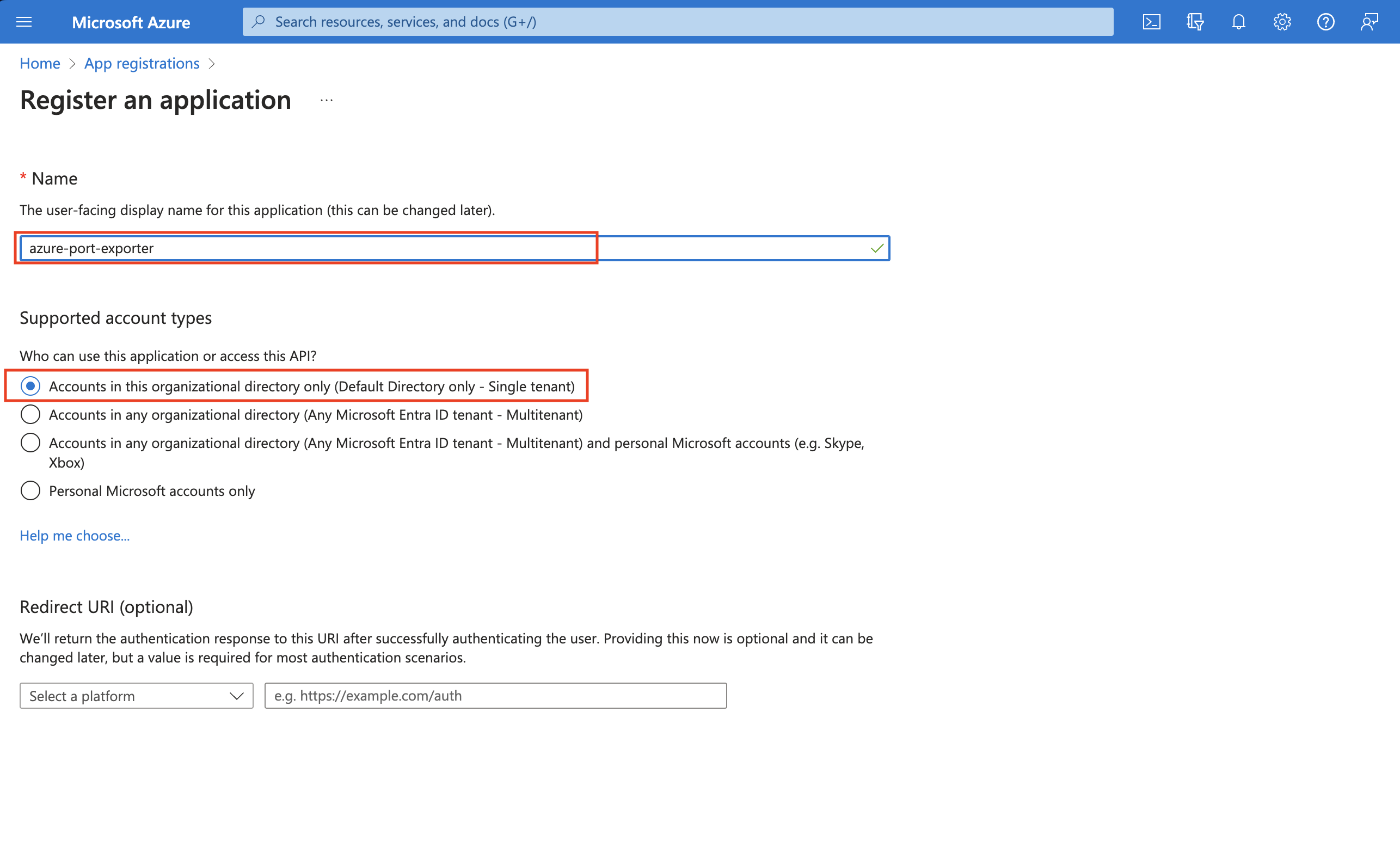
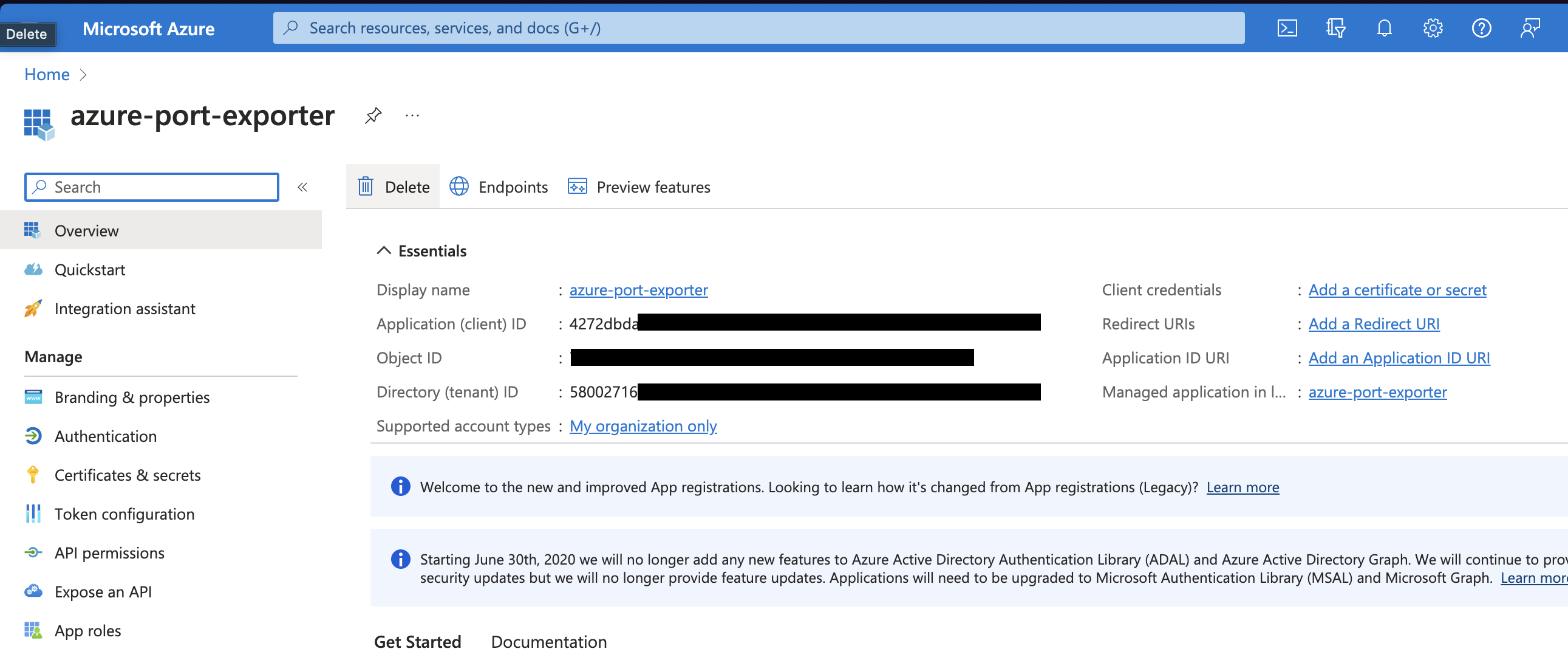
- Copy the
Application (client) IDandDirectory (tenant) IDfrom the App Registration.
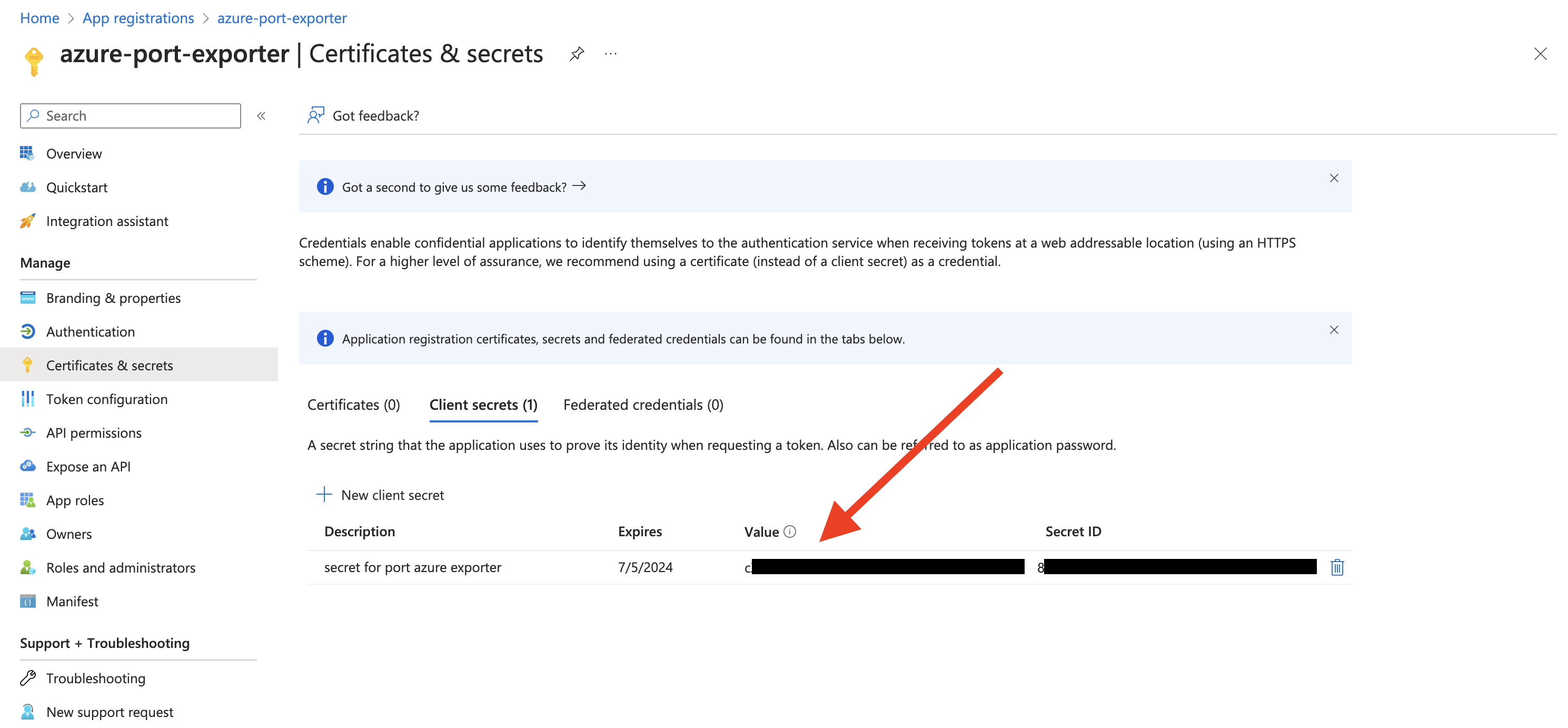
- Create a client secret for the App Registration.
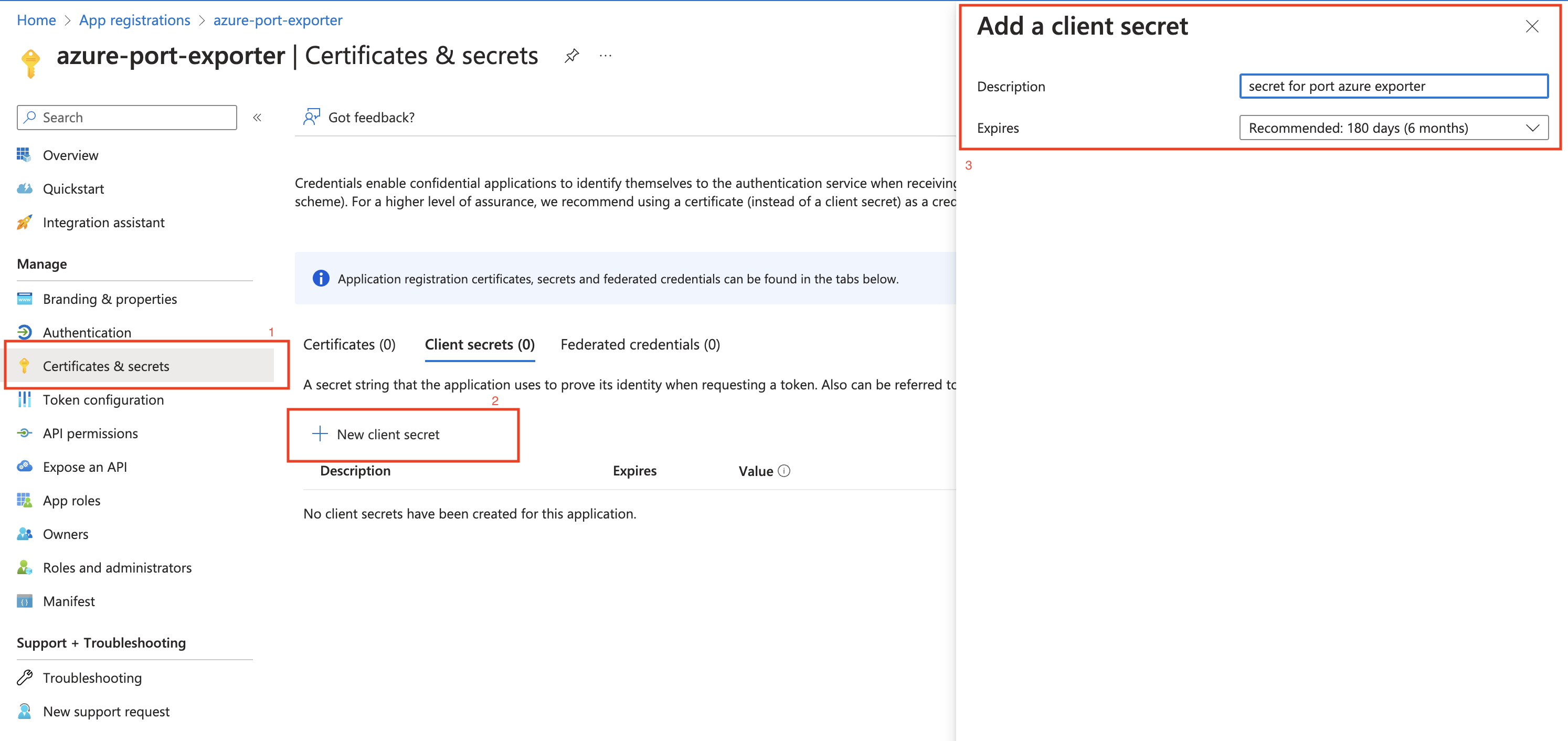
- Copy the
Application (client) Secretfrom the App Registration.
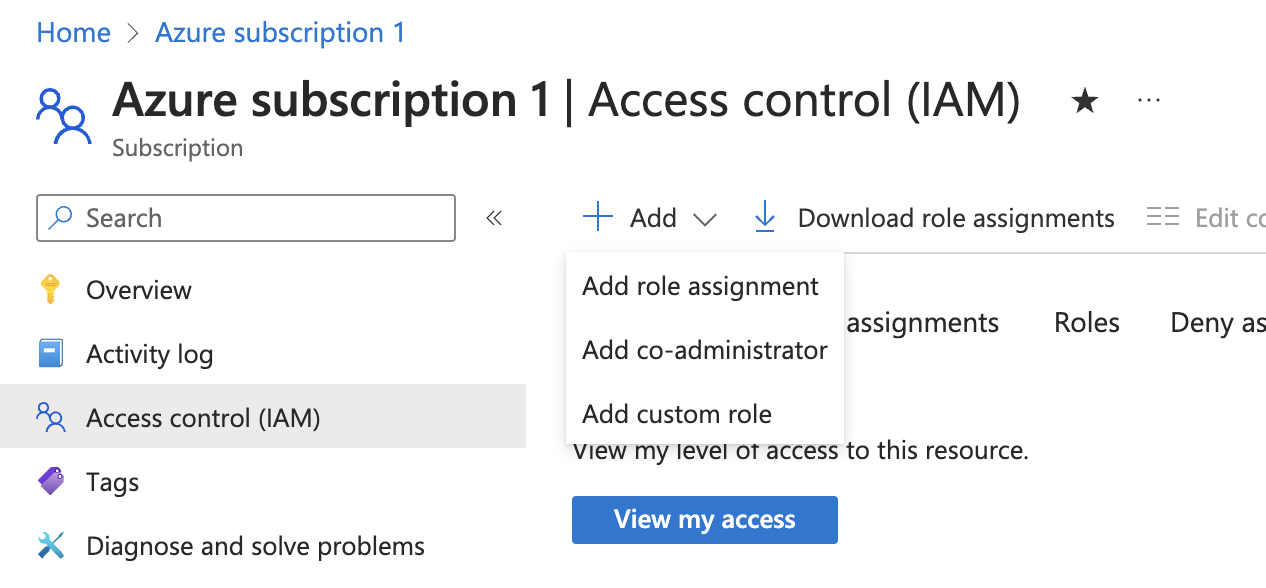
- Create a new role assignment for the App Registration. Go to the
Access control (IAM)section of the subscription you want to ingest resources from.
Click onAdd role assignment.
It is supported to ingest resources from multiple subscriptions, for that you will have to repeat the role assignment for each subscription you want to ingest resources from.
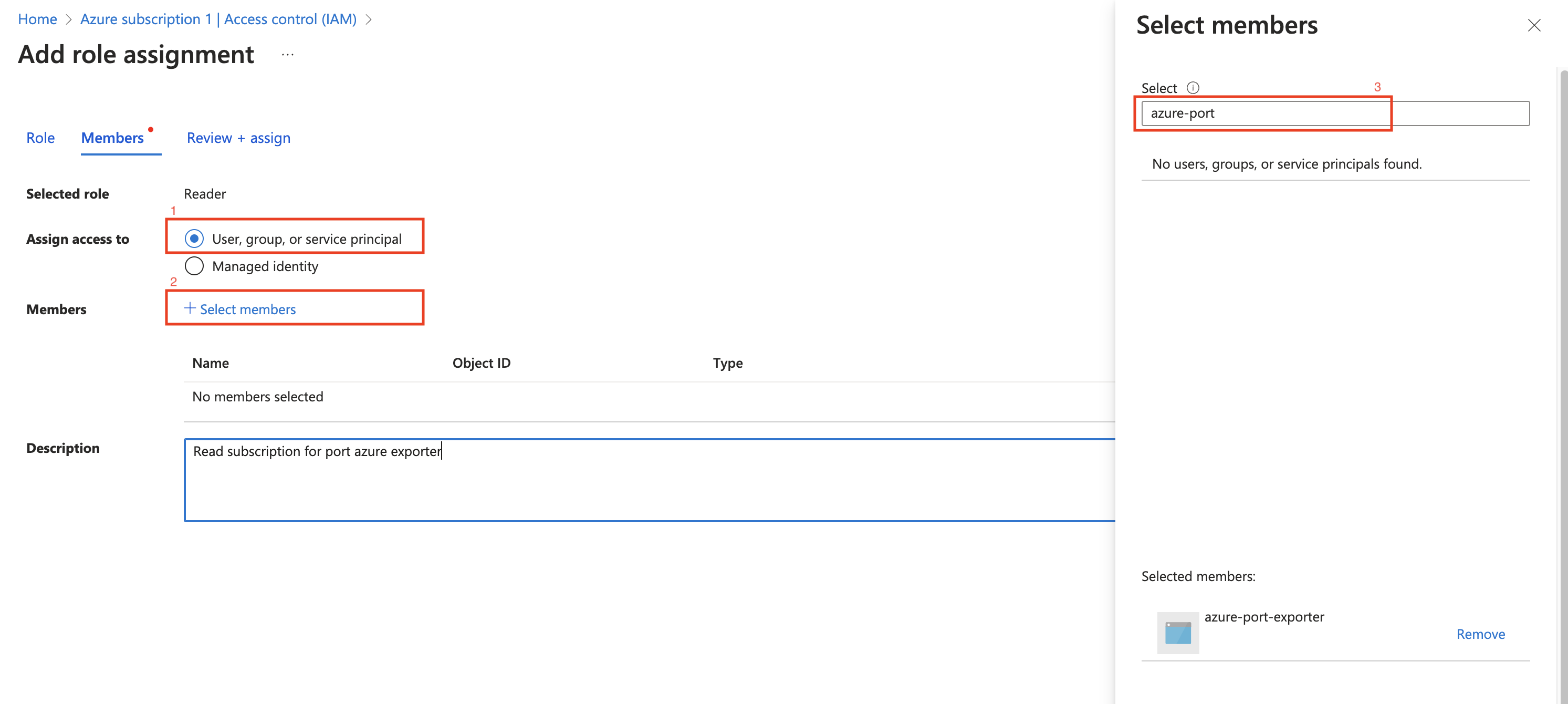
- Assign the
Readerrole to the App Registration.
The Reader role is recommended for querying all resources in your Azure subscription. You can restrict permissions to specific resource groups or types by assigning a different role. If you do this, remember to adjust permissions when adding more resources to the catalog. Basic permissions required for ingesting resources from Azure include:
Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/read(to list the accessible subscriptions)Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read(to list the accessible resource groups)read/listpermissions to the resources you want to ingest
Port setup
The basic Port setup follows the standard installation guide. However, this integration uses a different webhook configuration for incremental syncing:
Port credentials
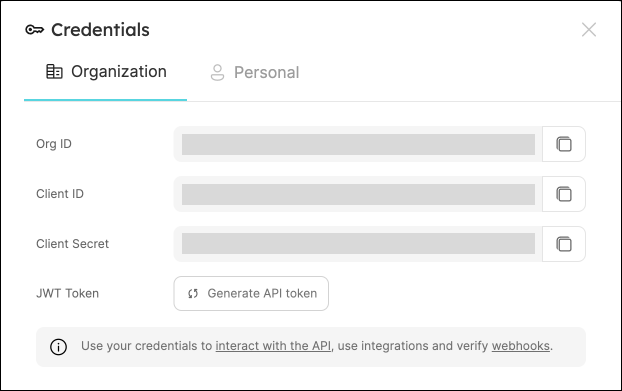
To get your Port credentials, go to your Port application, click on the ... button in the top right corner, and select Credentials. Here you can view and copy your CLIENT_ID and CLIENT_SECRET:
Blueprint configuration
While these configurations are provided as a starting point, you can customize them based on your specific requirements and the Azure resources you want to track.
Create the following blueprints in Port before syncing:
azureSubscription blueprint
{
"identifier": "azureSubscription",
"title": "Azure Subscription",
"icon": "Azure",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"subscriptionId": {
"title": "Subscription ID",
"type": "string"
},
"tags": {
"title": "Tags",
"type": "object"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {}
}
azureResourceGroup blueprint
{
"identifier": "azureResourceGroup",
"description": "This blueprint represents an Azure Resource Group in our software catalog",
"title": "Azure Resource Group",
"icon": "Azure",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"location": {
"title": "Location",
"type": "string"
},
"tags": {
"title": "Tags",
"type": "object"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"subscription": {
"title": "Subscription",
"target": "azureSubscription",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
}
azureCloudResources blueprint
{
"identifier": "azureCloudResources",
"description": "This blueprint represents an AzureCloud Resource in our software catalog",
"title": "Azure Cloud Resources",
"icon": "Git",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"tags": {
"title": "Tags",
"type": "object"
},
"type": {
"title": "Type",
"type": "string"
},
"location": {
"title": "Location",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": []
},
"mirrorProperties": {},
"calculationProperties": {},
"aggregationProperties": {},
"relations": {
"resourceGroup": {
"title": "Resource Group",
"target": "azureResourceGroup",
"required": false,
"many": false
}
}
}
Webhook configuration
To set up the webhook in Port:
- Navigate to the Data sources page.
- Click
+ Data Sourceand selectWebhook. - Fill in the required fields and create the webhook.
- Copy the webhook URL (you'll need this for the integration setup).
- Click Next to go the
Mappingsection. - Scroll down to find the
Map the data from the external system into Portsection.
Add the following webhook mapping in the Map the data from the external system into Port field:
Webhook Mapping Configuration
[
{
"blueprint": "azureCloudResources",
"operation": "create",
"filter": ".body.type == 'resource' and .body.operation == 'upsert'",
"entity": {
"identifier": ".body.data.resourceId | gsub(\" \";\"_\")",
"title": ".body.data.name",
"properties": {
"tags": ".body.data.tags",
"type": ".body.data.type",
"location": ".body.data.location"
},
"relations": {
"resourceGroup": "'/subscriptions/' + .body.data.subscriptionId + '/resourcegroups/' + .body.data.resourceGroup | gsub(\" \";\"_\")"
}
}
},
{
"blueprint": "azureCloudResources",
"operation": "delete",
"filter": ".body.type == 'resource' and .body.operation == 'delete'",
"entity": {
"identifier": ".body.data.resourceId | gsub(\" \";\"_\")"
}
},
{
"blueprint": "azureResourceGroup",
"operation": "create",
"filter": ".body.data.type == 'microsoft.resources/subscriptions/resourcegroups' and .body.operation == 'upsert'",
"entity": {
"identifier": ".body.data.resourceId | gsub(\" \";\"_\")",
"title": ".body.data.name",
"properties": {
"tags": ".body.data.tags",
"location": ".body.data.location"
},
"relations": {
"subscription": "'/subscriptions/' + .body.data.subscriptionId | gsub(\" \";\"_\")"
}
}
},
{
"blueprint": "azureResourceGroup",
"operation": "delete",
"filter": ".body.data.type == 'microsoft.resources/subscriptions/resourcegroups' and .body.operation == 'delete'",
"entity": {
"identifier": ".body.data.resourceId | gsub(\" \";\"_\")"
}
},
{
"blueprint": "azureSubscription",
"operation": "create",
"filter": ".body.data.type == 'microsoft.resources/subscriptions' and .body.operation == 'upsert'",
"entity": {
"identifier": ".body.data.resourceId | gsub(\" \";\"_\")",
"title": ".body.data.name",
"properties": {
"subscriptionId": ".body.data.subscriptionId",
"tags": ".body.data.tags"
}
}
},
{
"blueprint": "azureSubscription",
"operation": "delete",
"filter": ".body.data.type == 'microsoft.resources/subscriptions' and .body.operation == 'delete'",
"entity": {
"identifier": ".body.data.resourceId | gsub(\" \";\"_\")"
}
}
]
- The
body.operationfield is a discriminator for the webhook (not part of Azure resource payload) - The
body.typefield indicates the Azure resource type:resourcefor Azure resourcesresourceContainerfor resource containers (e.g., resource groups, subscriptions)
- The
body.datafield contains the Azure resource payload - The
body.data.typefield contains specific Azure resource types:microsoft.resources/subscriptions/resourcegroupsfor resource groupsmicrosoft.resources/subscriptionsfor subscriptionsmicrosoft.network/networksecuritygroupsfor network security groups
Resource group tag filtering
Filtering Azure resources by their parent resource group tags allows for precise, consistent, and efficient control over what gets synced to Port.
Resource groups typically have consistent, organization-wide tags, making them ideal for filtering. This approach:
- Avoids the need to tag every individual resource.
- Provides a consistent filtering mechanism.
- Reduces sync time and data volume by filtering at the query level.
Enhanced configuration format
You can specify both include and exclude tag filters in a single configuration object:
{
"include": {"Environment": "Production", "Team": "Platform"},
"exclude": {"Temporary": "true", "Stage": "deprecated"}
}
Configuration Examples
# Include only Production resources:
export RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS='{"include": {"Environment": "Production"}}'
# Include Production, exclude temporary:
export RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS='{"include": {"Environment": "Production"}, "exclude": {"Temporary": "true"}}'
# Include Platform team, exclude Development:
export RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS='{"include": {"Team": "Platform"}, "exclude": {"Environment": "Development"}}'
# Exclude only (no include):
export RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS='{"exclude": {"Environment": "Development", "Stage": "staging"}}'
# Complex multi-condition:
export RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS='{"include": {"Environment": "Production", "Team": "Platform"}, "exclude": {"Temporary": "true", "Purpose": "testing"}}'
Filter logic
- Include filters: All conditions must match (AND logic).
- Example:
{ "Environment": "Production", "Team": "Platform" }requires BOTH tags.
- Example:
- Exclude filters: Any condition matching will exclude (OR logic).
- Example:
{ "Temporary": "true", "Stage": "deprecated" }excludes if EITHER tag matches.
- Example:
- Combined: Resources must match all include criteria AND NOT match any exclude criteria.
- Defaults:
- Empty
include= include all (unless excluded). - Empty
exclude= exclude none.
- Empty
Tag matching rules
- Case-insensitive: Tag keys and values are matched case-insensitively.
- Exact value match: Tag values must match exactly (after case normalization).
- Missing tags: Resource groups missing required include tags are filtered out.
- Null/empty values: Treated as non-matches.
- Special characters: Properly escaped in tag values.
How filtering works
- Query-level filtering: Applied in Azure Resource Graph for optimal performance.
- Resource group join: Resources are joined with their parent RGs to access tags.
- Tag inheritance: Resource data includes both resource and RG tags (
rgTagsfield). - Dual application: Filtering applies to both resources and containers.
- Mode support: Works with both incremental and full sync.
- Filtering occurs in Azure, reducing data transfer.
- Fewer API calls and faster syncs.
- Only relevant resources are processed and sent to Port.
Installation methods
- GitHub Actions
- Local Installation
To run the integration using GitHub Actions, follow these steps:
-
Set up the following secrets in your GitHub repository:
AZURE_CLIENT_ID: The Azure service principal client IDAZURE_CLIENT_SECRET: The Azure service principal client secretAZURE_TENANT_ID: The Azure service principal tenant IDPORT_WEBHOOK_INGEST_URL: The webhook URL for ingesting Azure resources into Port
-
(Optional) Configure the following environment variables:
SUBSCRIPTION_BATCH_SIZE: Number of subscriptions to sync per batch (default: 1000, max: 1000)CHANGE_WINDOW_MINUTES: Time window for checking resource changes (default: 15 minutes)RESOURCE_TYPES: Specific Azure resource types to sync (default: All)# Example for specific resource types:
RESOURCE_TYPES='["microsoft.keyvault/vaults","Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks", "Microsoft.network/networksecuritygroups"]'RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS: Filter Azure resources by their parent resource group tags, see examples above
-
Create a GitHub workflow file based on your sync requirements:
- Incremental Sync
- Full Sync
This workflow runs automatically every 15 minutes to sync recent changes.
Create .github/workflows/azure-incremental-sync.yml:
name: "Incremental sync of Azure resources to Port"
on:
schedule:
- cron: "*/15 * * * *"
jobs:
sync:
name: Incremental sync
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Setup Python 3.12
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: "3.12"
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
ref: main
repository: port-labs/incremental-sync
- name: Install dependencies with Poetry
run: |
cd integrations/azure_incremental
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install poetry
make install
- name: Run incremental sync
run: |
cd integrations/azure_incremental
make run
env:
AZURE_CLIENT_ID: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }}
AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET }}
AZURE_TENANT_ID: ${{ secrets.AZURE_TENANT_ID }}
PORT_WEBHOOK_INGEST_URL: ${{ secrets.PORT_WEBHOOK_INGEST_URL }}
CHANGE_WINDOW_MINUTES: 15
# Optional: Enhanced resource group tag filtering
# RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS: ${{ secrets.RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS }}
This workflow can be triggered manually from the GitHub Actions UI.
It's recommended to run the full sync manually as it may take a long time to complete, depending on the number of Azure resources, subscriptions, and resource groups.
Create .github/workflows/azure-full-sync.yml:
name: "Full sync of Azure resources to Port"
on:
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
sync:
name: Full sync
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout Repository
uses: actions/checkout@v2
with:
ref: main
repository: port-labs/incremental-sync
- name: Install dependencies with Poetry
run: |
cd integrations/azure_incremental
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install poetry
make install
- name: Run full sync
run: |
cd integrations/azure_incremental
make run
env:
AZURE_CLIENT_ID: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }}
AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET }}
AZURE_TENANT_ID: ${{ secrets.AZURE_TENANT_ID }}
PORT_WEBHOOK_INGEST_URL: ${{ secrets.PORT_WEBHOOK_INGEST_URL }}
SYNC_MODE: full
# Optional: Enhanced resource group tag filtering
# RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS: ${{ secrets.RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS }}
To run the integration locally, follow these steps:
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/port-labs/incremental-sync.git
cd integrations/azure_incremental
- Install dependencies using Poetry:
pip install poetry
make install
- Set the required environment variables:
# Required variables
export AZURE_CLIENT_ID="your-azure-client-id"
export AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET="your-azure-client-secret"
export AZURE_TENANT_ID="your-azure-tenant-id"
export PORT_WEBHOOK_INGEST_URL="your-port-webhook-url"
# Optional variables
export SUBSCRIPTION_BATCH_SIZE=1000 # Default: 1000 (max)
export CHANGE_WINDOW_MINUTES=15 # Default: 15 minutes
export RESOURCE_TYPES='["microsoft.keyvault/vaults","Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks"]' # Default: All
export RESOURCE_GROUP_TAG_FILTERS='{"include": {"Environment": "Production"}}' # By default, all resource groups are included unless you set filters.
- Run the integration:
# For incremental sync
make run
# For full sync
export SYNC_MODE=full
make run
For development and testing purposes, you can use a smaller CHANGE_WINDOW_MINUTES value to sync changes more frequently.
How it works
The integration follows these steps:
- Fetches Azure subscriptions accessible to the Azure app.
- Queries changes in Azure resources within these subscriptions.
- Constructs and ingests resource groups into Port.
- Processes resource changes (create/update/delete) according to webhook configuration.
Next Steps
- Refer to the Resource Templates page for templates on how to map Azure resources to Port.